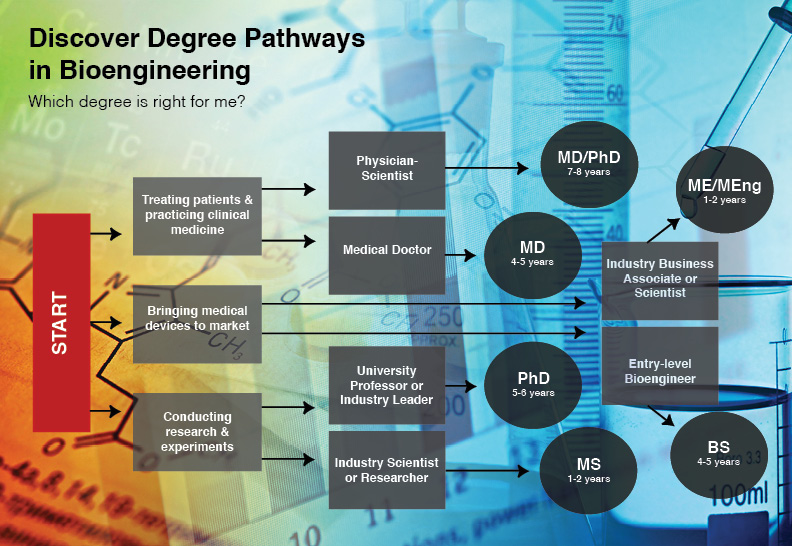
Degrees
Determining which academic degree is most appropriate for you depends on your personal and professional goals. Many people find satisfying careers in a variety of positions with a bachelor’s degree. Others find that a master’s degree equips them well for professional careers. For those who want to pursue careers conducting research and/or teaching at the university level, a Ph.D. will be required. Explore the chart below to learn about each degree, including career outcomes.
Key Differences Between Undergraduate and Graduate School
Funding
Paying for an undergraduate degree education is largely dependent on an individual student’s resources, scholarship opportunities, and loans. Students in graduate degree programs are often fully funded by multiple sources such as teaching assistantships, research assistant positions, or fellowships.Focus on Research
Coursework and exams are the main focus of undergraduate students in biomedical engineering, whereas conducting your own research is the focus of a graduate student in this field.Advising
Graduate students are required to identify a faculty advisor whom they will work with throughout their graduate education that has similar research interests.Independence
As an undergraduate student, much of your time is scheduled around classes and labs. As a graduate student, your time will be largely unstructured and will allow you to create your own timelines and deadlines.Questions for Selecting a Bioengineering Program
Questions and Answers
What is a PE license?
A PE (Professional Engineer) is a certification by a state board of registration to practice engineering. To become licensed, engineers must complete a four-year college degree, work under a Professional Engineer (PE) for at least four years, pass two competency exams and earn a license from their state’s licensure board. PEs must continually maintain and improve their skills throughout their careers to retain their license. PE’s already have thriving professional careers in engineering and acquire a license to enhance their career options. Biomedical engineering is not currently an available PE exam topic. Some biomedical engineers choose exams in chemical or mechanical engineering to become licensed.
How important is ABET Accreditation?
Accreditation, conducted by an independent review body, verifies that academic programs have met certain quality and performance standards in a specific profession. Prospective students can review ABET accreditation criteria to determine the importance of this standard for their intended career path. ABET accreditation serves a signal that the academic program is align with professional standards for the field. Choosing an ABET accredited program is desirable and it is a requirement for obtaining a Professional Engineer (PE) licensure. It is important to note that the American Board for Engineering and Technology (ABET) only accredits bachelor’s and master’s degree programs, not doctoral programs.
How do I select a training program in bioengineering?
Research opportunities, course opportunities, and career path guidance are the most important factors in selecting an undergraduate or graduate program in bioengineering. However, the surrounding environment and opportunities for community involvement are factors to consider as well. Meet with program graduates and learn about their experiences and career paths. Talk with faculty members at institutions of interest to learn about their research and decide if these areas interest you. Explore funding mechanisms like scholarships and teaching assistantships to help decipher how much the program will cost to attend. Meet with career counselors to discover the career outcomes of students attending particular programs. Search the websites of programs of interest and learn about their specific degree requirements and areas of focus. Finally, utilize the program search tool [link].
What are some major trends in higher education?
(1). Interdisciplinary programs.
Bioengineering is an inherently interdisciplinary field and higher education programs at colleges and universities reflect this. Students in degree programs in bioengineering may take classes in multiple departments within a single institution, as well as at other colleges across town or across the globe. They may also earn their degree from a joint program, encompassing more than one institution.
(2). Increased enrollment.
Enrollment in bioengineering programs at the bachelor’s, master’s, and doctoral levels have grown significantly.
